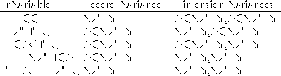
Table 3.1: Example rVariables, CDFstats Monotonicity Checking




The CDFstats program produces a statistical report on a CDF's variable data. Both rVariables and zVariables are analyzed. For each variable it determines the actual minimum and maximum values (in all of the variable records), the minimum and maximum values within the valid range (if the VALIDMIN and VALIDMAX vAttributes and corresponding entries are present in the CDF), and the monotonicity. An option exists to allow fill values (specified by the FILLVAL vAttribute) to be ignored when collecting statistics.
Monotonicity refers to whether or not variable data values increase or decrease from record to record or along a dimension. This property is checked only if the variable varies along just one ``dimension'' (considering records to be another ``dimension''). For example, consider a CDF with the 2-dimensional rVariables shown in Table 3.1.
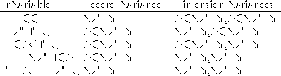
Table 3.1: Example rVariables, CDFstats Monotonicity Checking
The EPOCH, LATITUDE, and LONGITUDE rVariables would be checked for monotonicity but the ELEVATION and TEMPERATURE rVariables would not be checked.
An additional option exists that allows the VALIDMIN, VALIDMAX, SCALEMIN, and SCALEMAX attribute entries to be updated based on the actual minimum and maximum values found for a variable. The MONOTON attribute entries may also be updated based on the monotonicity found for a variable.